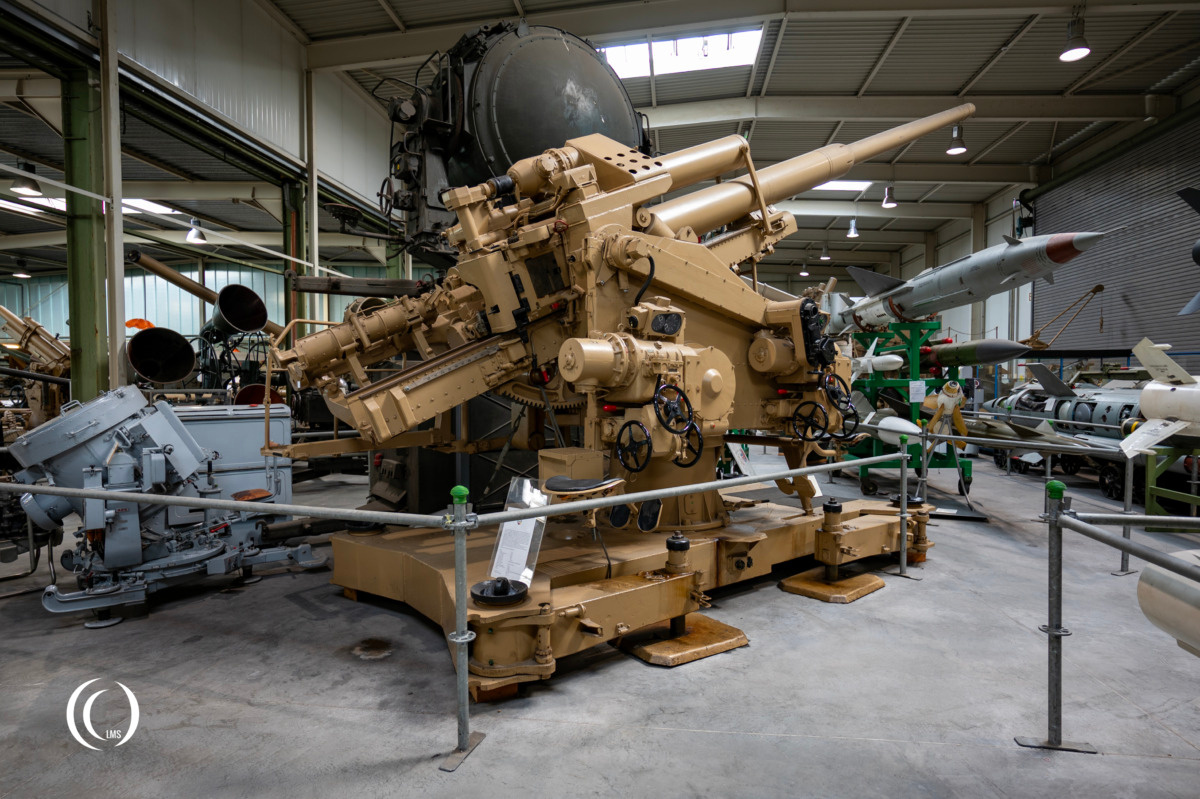

The Flak 12.8 cm 40 is a German heavy anti-aircraft artillery gun, or Schwerer Flugabwehrkanone, primarily used for engaging aerial targets using indirect aiming methods. It could also be aimed directly at ground or naval targets using the Flak Z.F. (Zielfernrohr) 20 E optic sight.
The heavy AA gun was the most important German anti-aircraft gun of the Wehrmacht during World War Two in a caliber over 10 cm. It served to protect important facilities against high-flying Allied bombers and was used in large cities on anti-aircraft towers, called Flakturme in German, like the Type VI G FlaKturm at Wilhelmsburg, Hamburg, Germany.
Its smaller sister the 8.8 cm FlaK 18/36/37 anti-aircraft gun was one of the most feared weapons on the World War Two battlefield, with a reputation for being highly effective against ground targets and armor.
Development
The gun was developed by Rheinmetall-Borsig between 1936 and 1940. A total of 1129 guns of this type were produced until 1945 by Rheinmetall and other manufacturers like F. Krupp AG in Essen, the Škoda plants in Pilsen, the Hanomag in Hanover and the Oberschlesische Gerätebau GmbH in Laurahütte. The FlaK 40/1 in these pictures was manufactured by Krupp AG in Essen and is on display at the Wehrtechnische Studiensammlung in Koblenz, Germany.
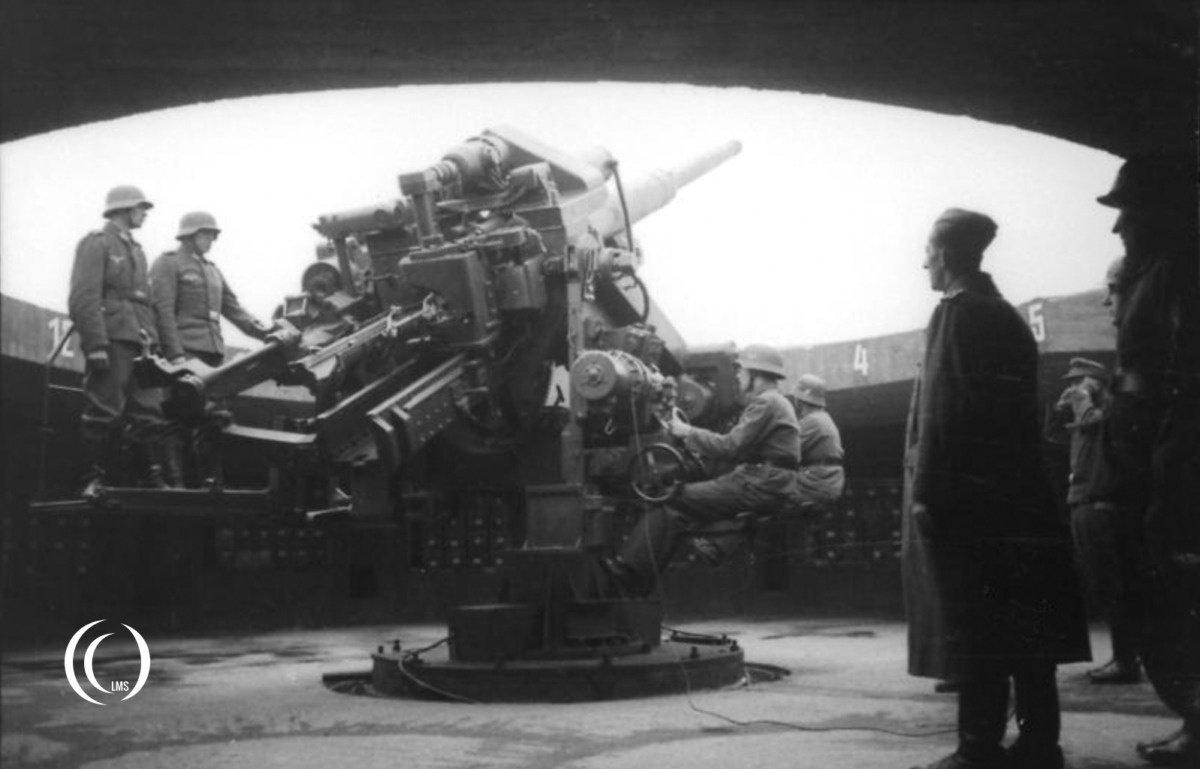

Operation
This Flak gun fired cartridge-case ammunition:
- Aerial targets were engaged using time-fuzed shells.
- Ground and naval targets were engaged using impact-detonated or contact-delay shells.
The time fuzes of the shells were set by a fuze-setting machine attached to the gun, based on values transmitted by the fire control computer like the Kommandogerät 40. The shells were then automatically loaded using an electrically driven loading system and fired electrically.
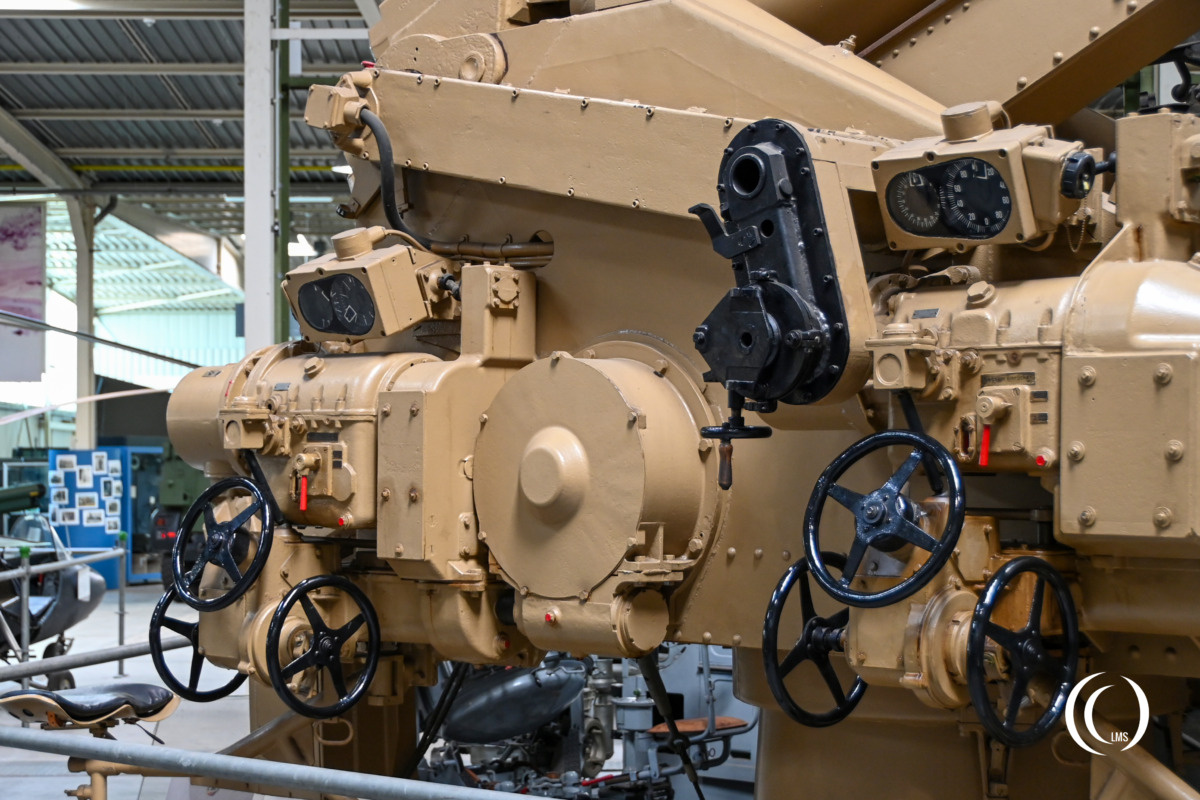


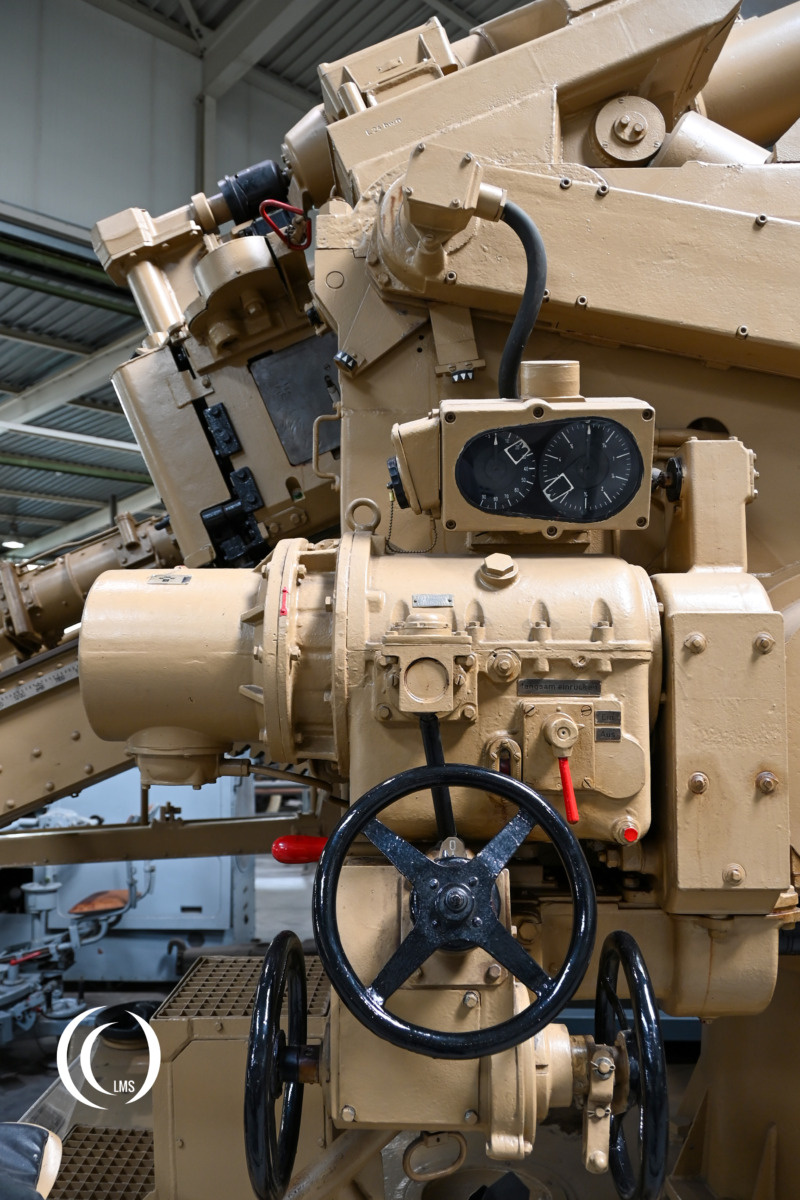
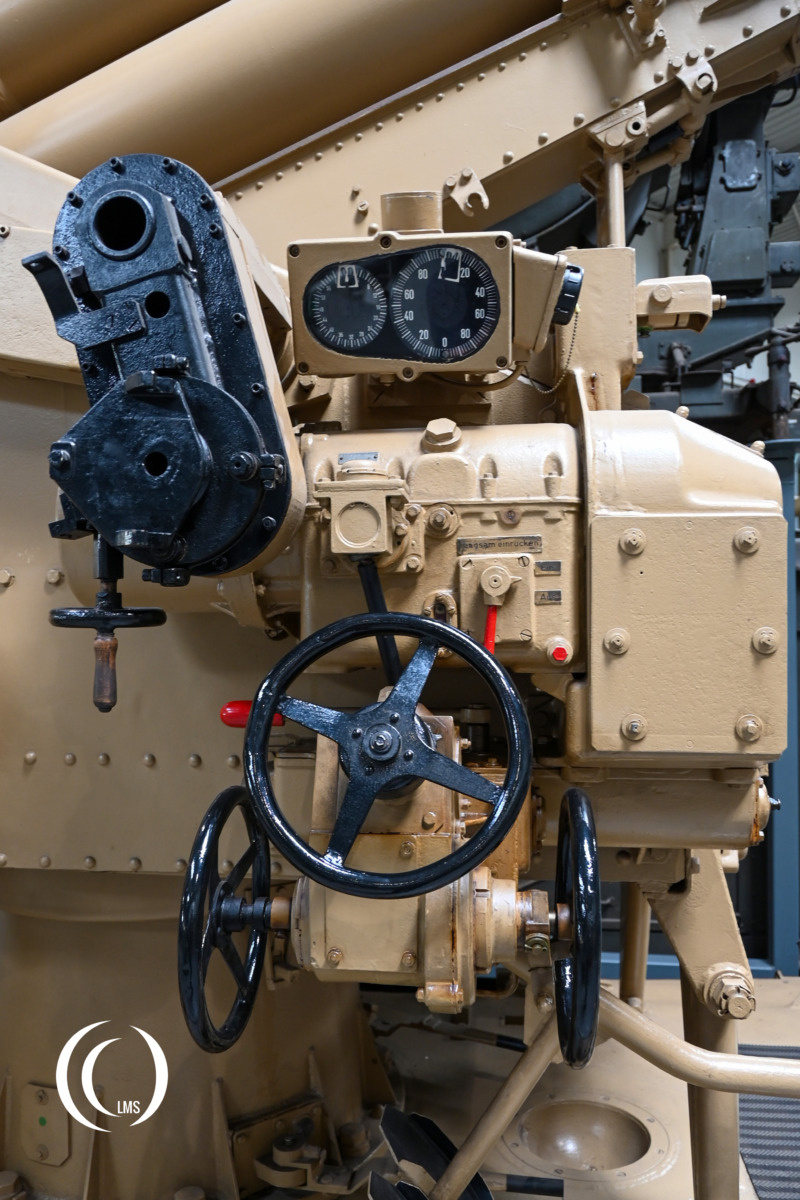
The gun’s aiming was achieved continuously via a hydraulic transmission system, but it could also be manually aimed if needed.
The barrel consisted of the inner barrel (bore tube), the outer casing (jacket tube) with bayonet ring, the breech block with breech ring and trunnion block and a recoil mechanism with tension screw, barrel clamp, and protective shield.
The weapon used a semi-automatic horizontal sliding breech for electrical firing with a hand-crank trigger mechanism.

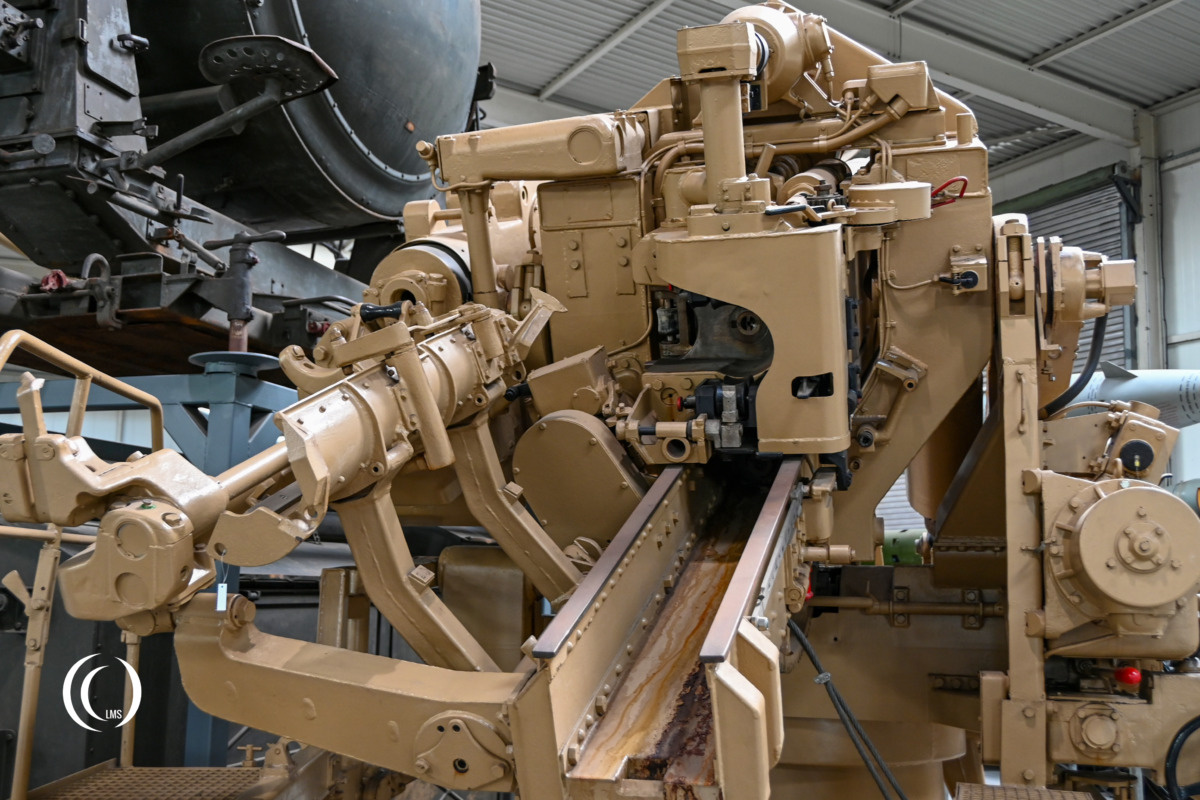
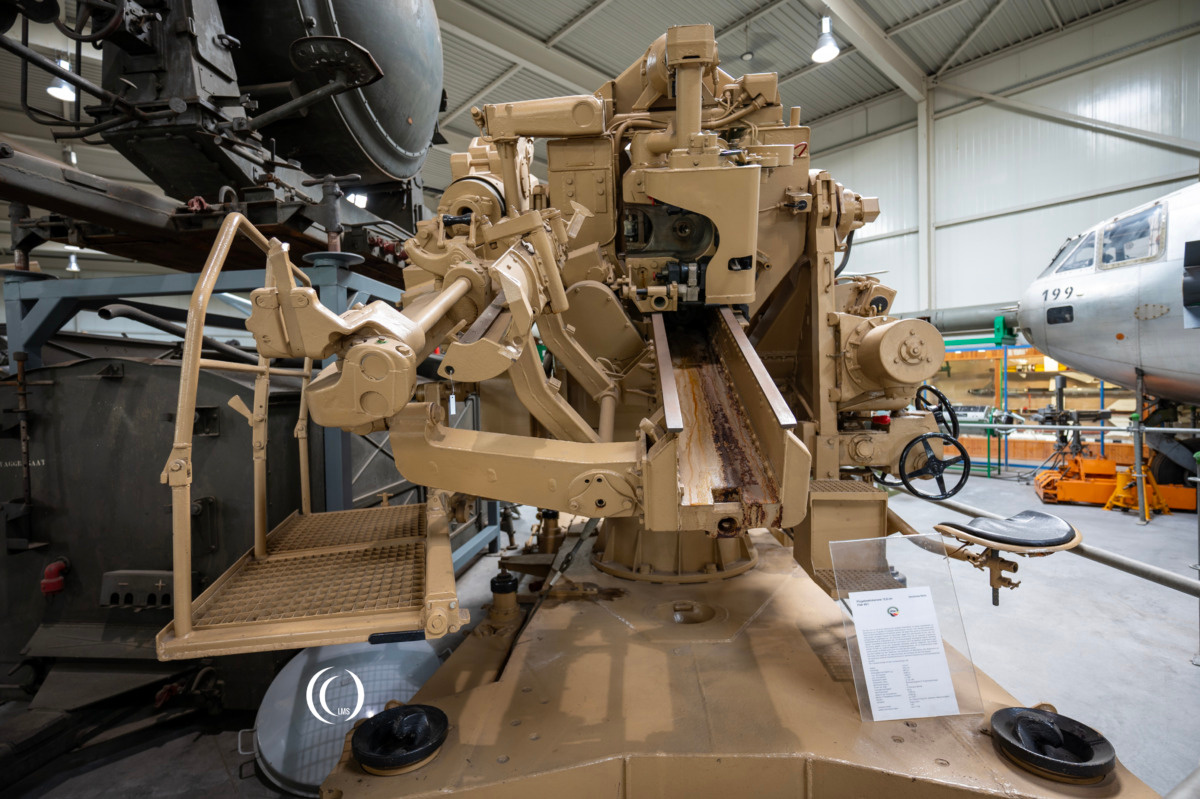
Specifications
- Caliber
12.8 cm - Barrel length
783.5 cm - Muzzle velocity (v₀)
880 m/s - Maximum range
20,950 m - Maximum altitude
14,800 m - Traverse range
n × 360° - Elevation range
-3° to +88° - Fire control data transmission
Transmission device 37 (indicator system) - Number of rifling grooves
40 - Rate of fire
12 rounds per minute - Shell weight
26 kg - Barrel weight
17,000 kg - Total weight (on Sd.Ah)
27,000 kg - Year of manufacture
1943 - Manufacturer
Friedrich Krupp AG, Steelworks, Machine Factory, Essen (bwn)

Transport
The transport of the gun was carried out using the special trailer Sd.Ah 220.
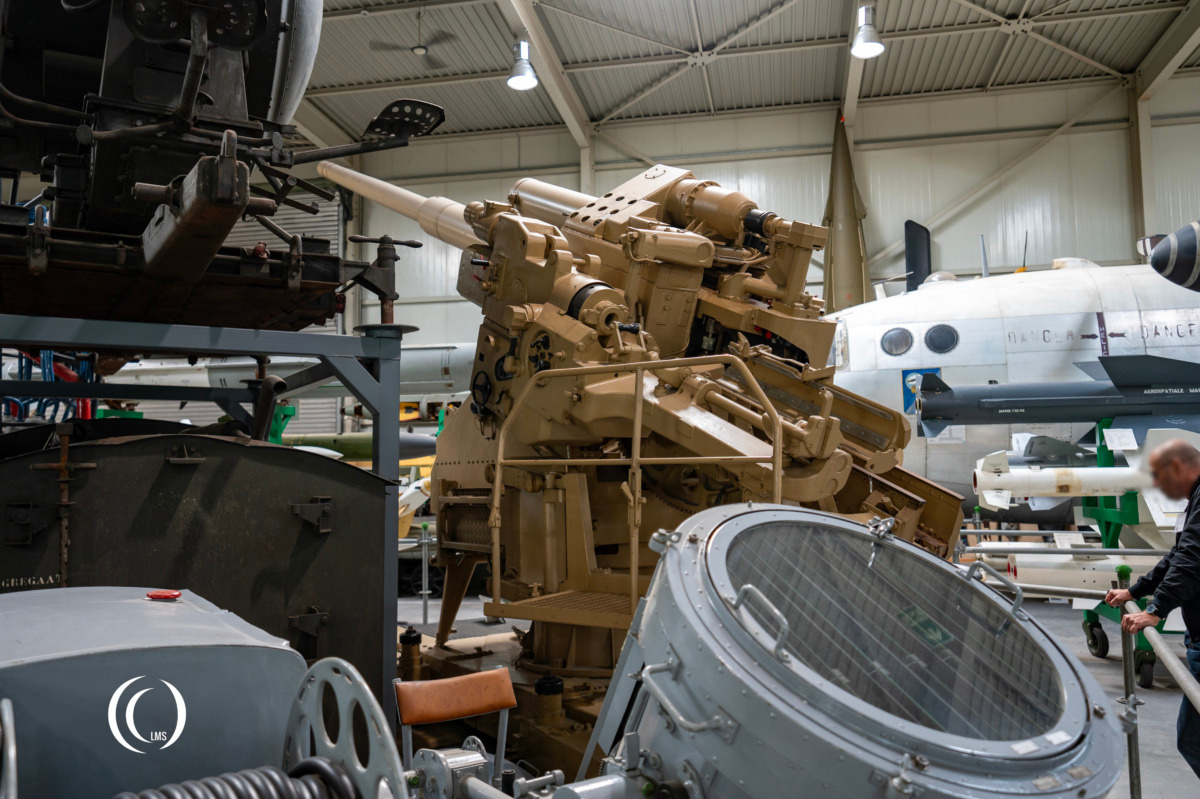

FlaK 40 variants
The FlaK 40 was produced in multiple variants:
- 12.8 cm Flak 40/1
- 12.8 cm Flak 40/2 Zwilling (Eng: twin – double-barred gun)
- 12.8 cm Flak 40/4 (Mounted on railway cart)
- 12.8 cm Flak 40/M (Kriegsmarine)